Understanding Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) should not be a barrier for professionals who want to enhance their laboratory operations.
Yet often, it is.
You may have a clear objective to enhance accuracy and speed in your laboratory, but the technical aspects of a Laboratory Information Management System can deter even the most enthusiastic professionals.
Breakthroughs in lab technology are sometimes sidelined due to these hurdles.
But it doesn’t have to be this way.
Whether you are a lab technician, a scientist, or a project manager, understand this: You do not need a background in software engineering to benefit from a Laboratory Information Management System.
You can either work with a consultant or adopt user-friendly LIMS platforms that simplify rather than complicate your processes.
Achieving a high-tech, efficient lab operation should not be an elusive goal.
Embracing LIMS is easier than you might think, and our guide is designed to demystify this crucial technology for you.
What is a Laboratory Information Management System?
A Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) is a software system designed to streamline the management of laboratory data and operations. You can utilise it in various scientific and industrial settings, tackling the large volumes of data that have to be dealt with in pharmaceuticals, healthcare, environmental science, manufacturing and research institutions.
Core Functionalities of LIMS – What LIMS is Capable Of
A Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) encompasses a range of features designed to streamline laboratory operations, manage data and ensure regulatory compliance.
Let’s take a deeper look.
- Sample Management: A Laboratory Information Management System provides comprehensive sample tracking capabilities, including sample accessioning, labelling, storage and retrieval. It assigns unique identifiers to each sample and maintains detailed records of sample information such as source, collection date and storage location, customer, lab, departments, etc.
- Data Management: A Laboratory Information Management System organises and manages vast amounts of laboratory data generated from various sources, including instruments, experiments and analyses. It consolidates all your laboratory data into a single repository, therefore ensuring data integrity, security and accessibility.
- Workflow Automation: A Laboratory Information Management System automates laboratory workflows by defining and enforcing standard operating procedures (SOPs) for sample processing, testing and analysis. It streamlines tasks such as sample registration, test scheduling, result recording and reporting (with or without electronic signatures and approvals), reducing manual errors and improving efficiency.
- Instrument Integration: A Laboratory Information Management System integrates with laboratory instruments and equipment to facilitate seamless data exchange and analytical processes. The automation of data capture in LIMS enables direct communication between instruments and the system, eliminating the need for any manual data entry from your part and in-turn reducing transcription errors.
- Quality Control: A Laboratory Information Management System incorporates robust quality control measures to ensure the accuracy, reliability and consistency of laboratory results. It supports the implementation of quality assurance protocols, such as instrument calibration, method validation, proficiency/competency testing and deviation management.
- Inventory Management: A Laboratory Information Management System manages laboratory inventory, including reagents, consumables and equipment. It tracks inventory levels, monitors usage and facilitates procurement and replenishment processes to ensure adequate supplies for your laboratory operations.
- Result Reporting: LIMS generates comprehensive reports and certificates of analysis (CoAs) for test results, ensuring that you get timely and accurate reporting. It supports customizable report templates, data visualisation tools and integration with external systems for result dissemination.
- Regulatory Compliance: A Laboratory Information Management System helps laboratories comply with regulatory requirements and industry standards such as GLP (Good Laboratory Practices), GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices), ISO (International Organization for Standardization) and FDA (Food and Drug Administration) regulations. It maintains detailed audit trails, version control and documentation for regulatory inspections and audits.
- Integration and Interoperability: LIMS integrates with other lab systems and enterprise applications, such as ELN (Electronic Laboratory Notebook), LIS (Laboratory Information System), ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and CRM (Customer Relationship Management), eliminating data silos and hence enabling seamless data exchange and interoperability across the organisation.
By centralising and automating these processes, the software will help you with the improvement of efficiency, accuracy and productivity during your lab operations.
Overall, LIMS plays a crucial role in modern laboratories by optimising workflows, managing data effectively, ensuring quality and compliance and facilitating informed decision-making processes.
Role of a Laboratory Information Management System as Opposed to Other Software in a Lab
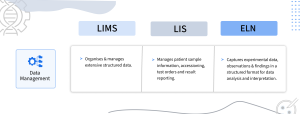
Commonly used software in a laboratory are LIMS (Laboratory Information Management System), LIS (Laboratory Information System) and ELNs (Electronic Laboratory Notebook). But to reap maximum benefits out of them, it is necessary for you to look at the comparison of their purpose.
- Purpose:
– LIMS (Laboratory Information Management System): Primarily focuses on managing laboratory samples, data, and workflows. It streamlines processes related to sample tracking, data management, and quality control.
– LIS (Laboratory Information System): Specialized for clinical and healthcare laboratories, focusing on managing patient information, test orders, and results. It ensures compliance with regulatory standards and integrates with electronic health records (EHR) systems.
– ELN (Electronic Lab Notebook): Aimed at documenting experimental procedures, observations, and results in research and development laboratories. It facilitates collaboration among researchers and enables data analysis and sharing.

- Sample Management:
– LIMS (Laboratory Information Management System): Provides extensive sample tracking capabilities, manages sample storage, and records sample metadata throughout its lifecycle.
– LIS (Laboratory Information System): Manages patient sample information, including sample accessioning, test orders, and result reporting in clinical settings.
– ELN (Electronic Lab Notebook): May include basic sample tracking features, but its primary focus is on documenting experimental procedures and results rather than managing physical samples.

- Data Management:
– LIMS (Laboratory Information Management System): Organizes and manages large volumes of structured laboratory data, including test results, instrument data, and sample information.
– LIS (Laboratory Information System): Manages patient data, test results, and diagnostic information, ensuring accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards in clinical laboratories.
– ELN (Electronic Lab Notebook): Captures experimental data, observations, and research findings in a structured format, facilitating data analysis, and interpretation.
- Workflow Automation:
– LIMS (Laboratory Information Management System): Automates laboratory workflows, including sample processing, testing, and result reporting (with electronic signature), to improve efficiency and reduce manual errors.
– LIS (Laboratory Information System): Streamlines clinical laboratory workflows, automating processes such as test ordering, specimen processing, and result verification to enhance productivity and patient care.
– ELN (Electronic Lab Notebook): Provides workflow templates and automation tools for documenting experimental procedures, enabling researchers to follow standardized protocols and workflows.

- Integration with Instruments:
– LIMS (Laboratory Information Management System): Integrates with laboratory instruments and equipment to automate data capture, analysis, and result reporting, ensuring data accuracy and consistency.
– LIS (Laboratory Information System): Interfaces with diagnostic instruments and laboratory analyzers to receive and process test results, facilitating seamless integration with laboratory workflows.
– ELN (Electronic Lab Notebook): May offer limited integration with laboratory instruments for data capture and analysis but is primarily focused on documenting experimental procedures and results.

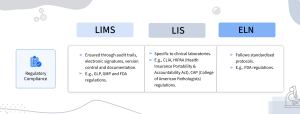
- Regulatory Compliance:
– LIMS (Laboratory Information Management System): Ensures compliance with regulatory standards and industry regulations, such as GLP, GMP, and FDA requirements, through audit trails, electronic signature, version control, and documentation.
– LIS (Laboratory Information System): Adheres to regulatory standards specific to clinical laboratories, such as CLIA, HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and CAP (College of American Pathologists) accreditation requirements.
– ELN (Electronic Lab Notebook): Supports compliance with research standards and guidelines, such as FDA regulations for laboratory data integrity and documentation practices.
This section has illustrated the critical role of a Laboratory Information Management System and how it distinctly positions itself against other laboratory software like LIS and ELN. Each system has its unique strengths tailored to specific laboratory needs — LIMS with its comprehensive sample and data management designed for a variety of lab environments, LIS focusing on clinical specifics and patient-centric data, and ELN enhancing the documentation and collaboration in research settings.
More than mere technology, digital transformation in the lab setting is about equipping the workforce with the right tools to enhance operational efficiencies and decision-making. Success in modern labs is increasingly dependent on the ability to generate and utilize data effectively, allowing for dynamic adaptation to market needs.
In this context, LIMS emerges not just as a tool, but as a pivotal component of digital transformation, unlocking significant value for laboratories. It boosts agility, ensures compliance, and enhances data integrity, positioning businesses to innovate and scale swiftly, meeting the rapidly evolving demands of the scientific and medical landscapes.
Stakeholders that will benefit from a Laboratory Information Management System
Implementing the LIMS software in a lab will benefit various individuals, organisations and industries. Take a look at the following stakeholders of the system to see how you will benefit depending on your role in accordance with the system:
- Laboratory Managers and Technicians: These professionals directly interact with the Laboratory Information Management System on a day-to-day basis to manage laboratory operations. The instrument helps them streamline processes, improve efficiency and ensure data accuracy in their day-to-day work.
- Researchers and Scientists: In research and development laboratories, scientists and researchers benefit from the Laboratory Information Management System by using it for experimental procedure documentation, research data management and collaboration. This system fosters data sharing, analysis and interpretation, enabling informed decision-making and accelerating scientific discoveries.
- Quality Assurance and Compliance Teams: Organisations in regulated industries, such as pharmaceuticals, healthcare and food and beverage, benefit from LIMS’ ability to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and industry regulations. LIMS helps quality assurance teams implement and enforce quality control measures, track deviations and maintain audit trails for regulatory inspections and audits.
- Healthcare Providers and Clinicians: Clinical laboratories and healthcare providers leverage LIS (Laboratory Information System), a specialised type of LIMS, to manage patient information, test orders and results. LIS facilitates efficient test ordering, specimen processing and result reporting, thus leading to enhanced patient care and clinical decision-making.
- Manufacturing and Production Managers: The Laboratory Information Management System supports quality control and production processes in manufacturing industries. It manages raw material testing, product quality analysis and batch tracking. This assists manufacturing and production managers in ensuring product consistency, meeting regulatory requirements and improving overall operational efficiency.
- Environmental Monitoring and Testing Agencies: Environmental laboratories benefit from the Laboratory Information Management System by managing sample analysis for environmental monitoring, water quality testing, air pollution monitoring and soil analysis. LIMS helps these agencies track samples, analyse environmental data and generate reports to support environmental protection and regulatory compliance efforts.
- Forensic Laboratories and Crime Investigation Units: Forensic laboratories use the Laboratory Information Management System to manage evidence tracking, chain of custody documentation and case management in criminal investigations. LIMS helps ensure the integrity and confidentiality of forensic data, supports legal proceedings and guarantees adherence to forensic standards and protocols.
- Academic and Research Institutions: Universities, research institutes and academic laboratories utilise LIMS to manage research projects, collaborate among interdisciplinary teams and track laboratory resources. LIMS supports academic research by facilitating data sharing, reproducibility and compliance with research standards and guidelines.
Overall, LIMS benefits a wide range of stakeholders across industries by improving laboratory efficiency, data management, compliance and decision-making processes. It enables organisations to enhance productivity, ensure data integrity and achieve your goals in laboratory operations, research and quality assurance.
Importance of a Laboratory Information Management System
The importance of Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) in lab management cannot be overstated. Here are several key reasons why LIMS is crucial for effective lab management:
- Streamlined Workflows: LIMS helps streamline laboratory workflows by automating routine tasks such as sample tracking, data entry, and result reporting using electronic signatures and approvals. This automation reduces manual errors, improves operational efficiency, and allows laboratory staff to focus on more critical tasks.
- Improved Data Management: A Laboratory Information Management System centralizes and organizes laboratory data, including sample information, test results, and instrument data. This centralized data management system ensures data integrity, accessibility, and traceability, facilitating efficient data analysis, interpretation, and decision-making.
- Enhanced Sample Tracking: With LIMS, laboratories can track samples throughout their lifecycle, from sample accessioning to storage, testing, and disposal. This capability ensures sample traceability, reduces the risk of sample mix-ups or loss, and supports compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Quality Control and Assurance: A Laboratory Information Management System incorporates quality control measures to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and consistency of laboratory results. It enables laboratories to implement quality control protocols, monitor instrument performance, and track deviations to maintain quality standards and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Compliance Management: A Laboratory Information Management System helps laboratories comply with regulatory standards and industry regulations, such as GLP, GMP, ISO, and FDA requirements. It maintains audit trails, version control, and documentation to demonstrate compliance during regulatory inspections and audits, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties and sanctions.
- Integration with Instruments and Systems: A Laboratory Information Management System integrates with laboratory instruments and systems to automate data capture, analysis, and reporting processes. This integration eliminates manual data entry errors, ensures data consistency, and improves interoperability between different laboratory systems and devices.
- Resource Optimization: By optimizing workflows, automating tasks, and improving data management, LIMS enables laboratories to optimize their resources, including personnel, equipment, and consumables. This optimization results in cost savings, increased productivity, and improved resource utilization in laboratory operations.
- Facilitated Collaboration: Laboratory Information Management System facilitates collaboration among laboratory staff, researchers, and external stakeholders by providing a centralized platform for data sharing, communication, and collaboration. It enables real-time access to laboratory data and results, fostering collaboration across interdisciplinary teams and external partners.
- Data Security and Confidentiality: Laboratory Information Management System employs robust security measures to protect sensitive laboratory data from unauthorized access, modification, or loss. It ensures data security and confidentiality, safeguarding intellectual property, patient information, and regulatory compliance in laboratory operations.
- Continuous Improvement and Decision Support: LIMS provides valuable insights into laboratory performance, trends, and metrics through reporting and analytics capabilities. This data-driven approach enables laboratories to identify areas for improvement, make informed decisions, and drive continuous quality improvement initiatives.
Overall, LIMS plays a vital role in modern lab management by improving efficiency, data management, quality control, compliance, and decision support. It enables laboratories to meet the challenges of today’s dynamic and highly regulated environment, ensuring the delivery of high-quality and reliable laboratory services.
Going Paperless with a Laboratory Information Management System
Achieving a paperless lab environment using Laboratory Information Management Systems involves leveraging the capabilities of LIMS to digitise and automate your laboratory processes, data management & documentation. As technology advances, LIMS will become an essential and modern tool for your laboratory. The system will further assist you with:
- Electronic Data Capture: This enables you to capture data automatically and directly from instruments, equipment and other digital sources. You will no longer have to manually record data on paper since the system integrates with laboratory instruments, ensuring accuracy and reducing any transcription errors.
- Digital Sample Management: A Laboratory Information Management System centralises and digitises your sample management processes, including sample accessioning, tracking and storage. You will no longer have to rely on paper-based sample logs and labels with the use of LIMS since it electronically manages your information and real-time location.
- Electronic Workflows: A Laboratory Information Management System automates your laboratory workflows by defining and enforcing standardised procedures electronically. LIMS digitises and manages all your workflows including sample processing, testing and result reporting and you will no longer have the need for paper-based protocols and manual intervention.
- Electronic Approvals and Signatures: LIMS supports electronic signatures and approvals, allowing hassle-free sign-off on documents and records electronically. Also keep in mind that only users authorised by you will get to do this, guaranteeing the integrity and traceability of your data. This eliminates the need for you to go through any extensive approval processes for physical signatures on paper documents.
- Digital Document Management: LIMS provides you with digital document management, reducing the burden of overflowing folder cabinets. All your laboratory protocols, SOPs, test methods and reports are electronically stored, organised, managed and accessed within the Laboratory Information Management System . This will reduce your reliance on paper-based documentation and will instantly digitise all your information.
- Electronic Reporting and Analysis: The Laboratory Information Management System generates electronic reports and analyses your laboratory data, test results and quality metrics. Gone are the days when you would have to rely on printing paper reports. With LIMS, you will be able to access and share electronic reports directly from the LIMS system, making data analysis, interpretation and decision-making hassle-free.
- Remote Access and Collaboration: The Laboratory Information Management System supports remote access and collaboration among laboratory staff, researchers and the rest of your stakeholders. Authorised users will be able to access your laboratory data and collaborate with you on projects from any location. Your physical presence in the laboratory will thus be reduced, enabling remote work and collaboration.
- Data Security and Compliance: LIMS ensures the security of your data and its compliance with regulatory standards and industry regulations in a paperless lab environment and will provide protection from unauthorised access, modification or accidental data erasure. Plus, a Laboratory Information Management System automatically maintains Audit trails and documentation so that you will be able to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Environmental Sustainability: By ditching paper-based documents, your utilisation of LIMS contributes to environmental sustainability. By going green in a paperless lab environment powered by LIMS, you will be actively minimising the environmental footprint of laboratory operations.
Overall, LIMS plays a critical role in achieving a paperless lab environment by digitising laboratory processes, data management & documentation. It improves efficiency, data integrity and compliance while contributing to environmental sustainability efforts.
Adopting Laboratory Information Management System to replace Legacy Applications
Adopting a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) to replace legacy applications is a pivotal step for modernizing lab operations.
But often, it is met with resistance.
Legacy systems might be familiar, but their limitations in scalability, efficiency, and integration are increasingly apparent. The transition to LIMS can seem daunting, plagued by the fear of complex data migrations and workflow disruptions.
Yet, the need for change is undeniable.
For laboratory managers, researchers, and IT professionals, understand this: transitioning to LIMS doesn’t require you to be an IT guru.
You can work alongside migration experts or choose LIMS solutions designed for ease of transition and user-friendliness.
Moving to a more advanced, integrated, and compliant system should not be seen as a hurdle, but as an opportunity for significant enhancement.
Embracing LIMS to replace outdated applications is less about technical challenge and more about strategic advancement.
Let’s see how.
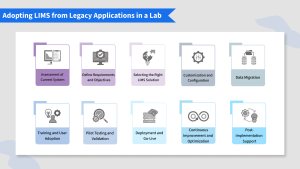
- Assessment of Current System:
It is important to evaluate the existing legacy system to identify its strengths, weaknesses and limitations. Determine the reasons for transitioning to a Laboratory Information Management System, such as outdated technology, scalability issues, regulatory compliance requirements, or workflow inefficiencies.
- Define Requirements and Objectives:
While defining your requirements and objectives for the new Laboratory Information Management System implementation, consider factors such as laboratory workflows, sample types, data management needs, regulatory compliance requirements, integration with instruments and systems and user preferences.
- Selecting the Right Laboratory Information Management System Solution:
Research and evaluate different Laboratory Information Management System solutions available in the market. Prioritise factors such as functionality, scalability, flexibility, ease of use, vendor support and cost.
- Customization and Configuration:
While the ability to customize and configure a Laboratory Information Management System differs from vendor to vendor, most minor changes that could help the LIMS align better and work with your existing systems are generally accommodated. Make sure to define data fields, user roles, access permissions and system configurations to align with your laboratory’s operations.
- Data Migration:
To ensure a seamless and less stressful retention of data that was documented in a relatively traditional manner, develop a data migration strategy, including data mapping, cleansing and validation, to ensure accurate and complete data transfer. Test the data migration process thoroughly to identify and address any issues or discrepancies.
- Training and User Adoption:
Getting used to a new system can be a little overwhelming in the get-go. To tackle this while adopting and effectively using LIMS, laboratory staff will require comprehensive training sessions, workshops and tutorials. Familiarise users with the system’s features, functionalities and best practices and encouraging user engagement & feedback will address any concerns or challenges in the beginning stages. Once that is accomplished, there will be seamless and skillful usage of the system in the long run.
- Pilot Testing and Validation:
Conduct pilot testing of the new LIMS in a controlled environment to evaluate its performance, functionality and usability. Involving key stakeholders and end-users in the pilot testing phase will aid in gathering feedback and identifying areas for improvement. Also, validate the system against regulatory requirements and quality standards to ensure compliance.
- Deployment and Go-Live:
It is finally launch day, where you deploy the new LIMS in the production environment. It is vital to coordinate with IT teams, vendors and stakeholders to ensure a smooth transition from the legacy system to the new LIMS. Monitor system performance and user feedback during the initial deployment phase and address any issues or concerns promptly.
- Continuous Improvement and Optimization:
Continuously monitoring and optimising the LIMS implementation will ensure its effectiveness, efficiency and alignment with laboratory goals and objectives. Gather user feedback, track key performance metrics and implement enhancements & updates as needed, for it will improve system functionality and your satisfaction.
- Post-Implementation Support:
Providing ongoing support and maintenance is essential for LIMS. This will ensure smooth operations and address any technical issues, user queries, or system updates. Establish a helpdesk or support system for assistance with troubleshooting, training and system enhancements. It is crucial to regularly review and update system documentation, SOPs & training materials to ensure relevancy.
By following these steps and engaging stakeholders throughout the process, laboratories can successfully adopt LIMS from a legacy system. The LIMS system will thus undoubtedly improve efficiency, data management & compliance, and to achieve your laboratory goals and objectives.
Bottomline
Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) have revolutionised the way laboratories operate, transforming traditional paper-based processes into efficient, digitised workflows. With LIMS, you can seamlessly enforce sample management, automate your workflows, improve data integrity and ensure compliance with regulatory standards in your lab. When you finally get to adopt LIMS, it will enable your laboratory to enhance productivity, reduce any errors during manual data management and assist you in making informed decisions based on reliable data.
Moreover, as technology continues to evolve, LIMS will play an increasingly vital role in driving innovation, collaboration and efficiency in your laboratory operations. For a robust and user-friendly LIMS solution, you can consider Agaram’s Qualis LIMS.
Qualis LIMS offers a comprehensive suite of features designed to streamline workflows, enhance data integrity, and empower your lab functions to achieve its full potential. With its emphasis on configurability and regulatory compliance, Qualis LIMS can be your powerful partner and boost innovation and scientific progress.
Learn more here.





